WBC Count
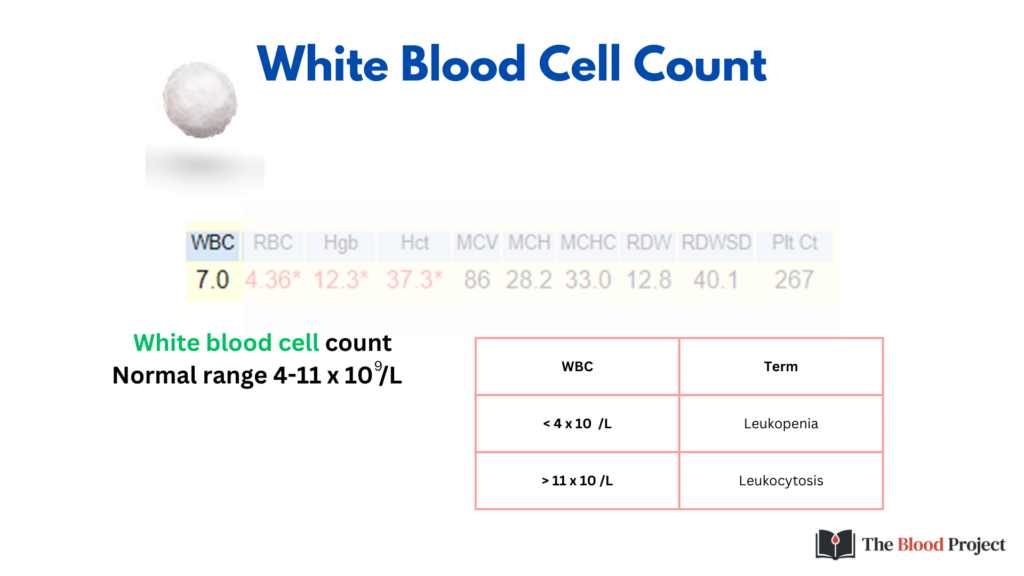
Here we are focusing on the WBC count. The WBC count in this patient is written as 7.0, which indicates:
- 7.0 x 109/L
- 7,000/ul
- 7.0 x 106 /ml
- 7.0 x 106/mm3
The normal range for the WBC count varies between laboratories but is generally 4-11 x 109/L.
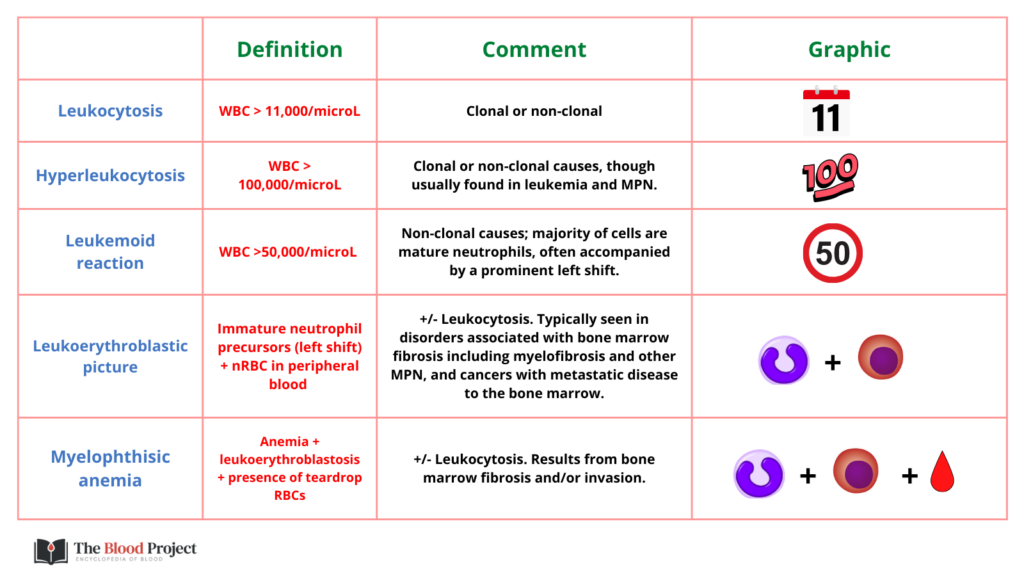
Abnormalities in WBC count include:
- Leukopenia (< 4 x 109/L)
- Leukocytosis (> 11 x 109/L)
We will return to related terms later in the course:
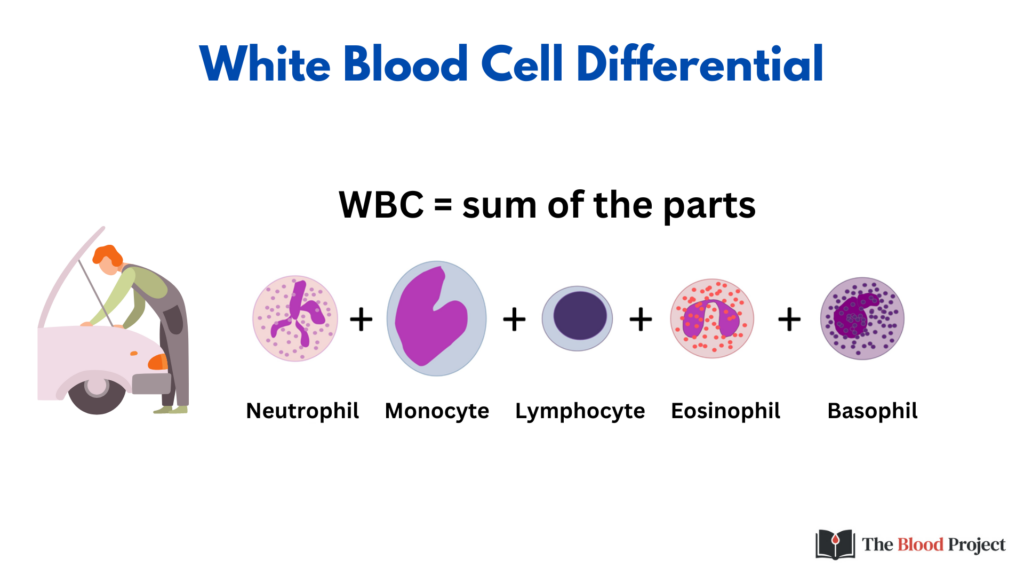
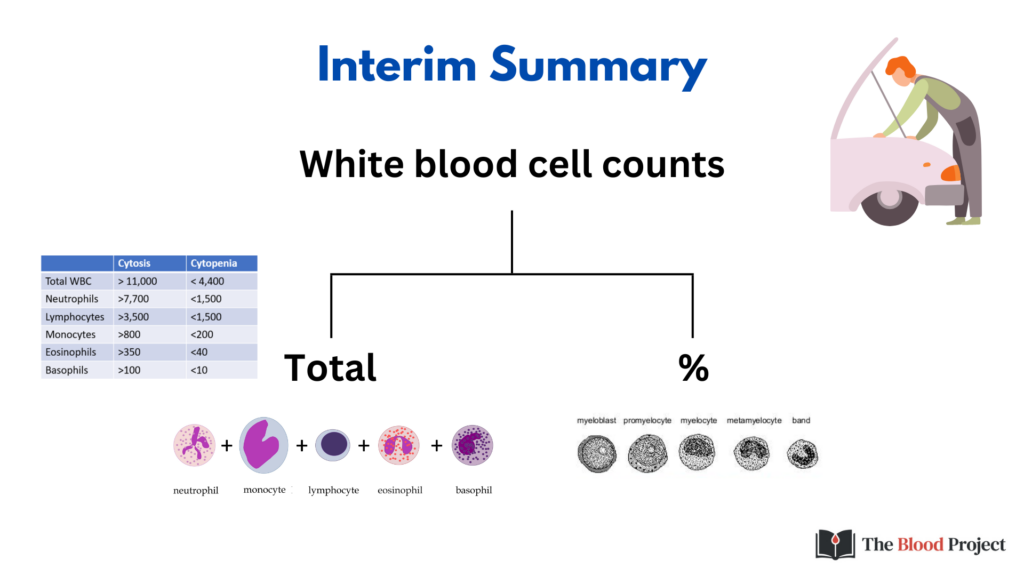
The WBC count is the sum of its parts. You must order a WBC differential separately from the basic CBC to enumerate the WBC subtypes, which normally include:
- Neutrophils
- Lymphocytes (B cells and T cells)
- Monocytes
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
Note about terminology:
- Granulocytes include neutrophils, eosinophils and neutrophils.
- Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) may refer to neutrophils, eosinophils and neutrophils or be used synonymously with neutrophils.

There are two ways of reporting the WBC differential:
- Percentage of total WBC count (adds up to 100%)
- Total count (absolute count) per volume (adds up to total WBC count)
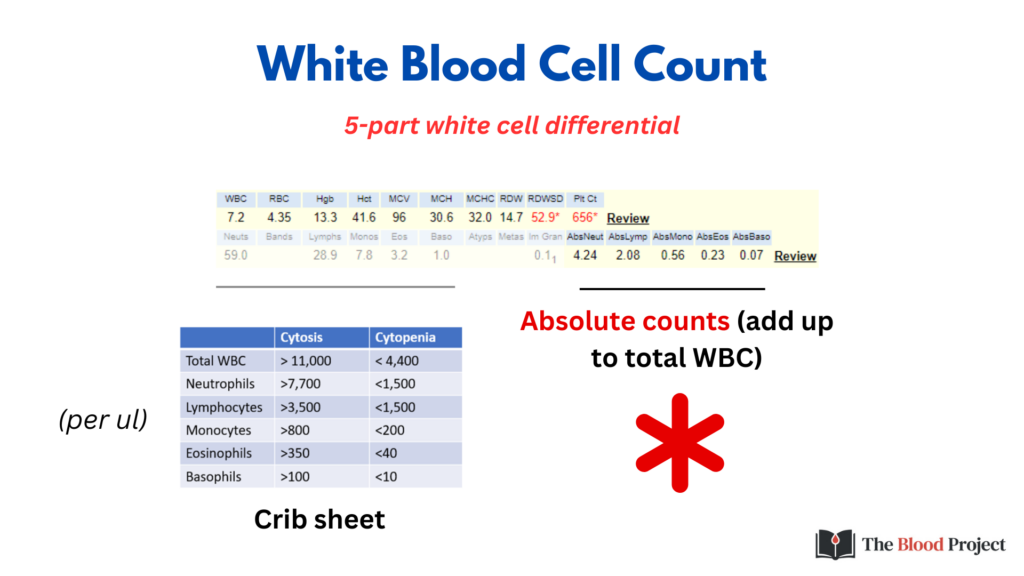
Whenever referring to the 5 mature subtypes of WBC, use absolute counts. It is the absolute count, not the percentage, that is used to define lower-than-normal (cytopenia) and higher than normal counts (cytosis):
| Cell subtype | Range | Term |
|---|---|---|
| Neutrophil | < 1.5 x 109/L | Neutropenia |
| > 7.7 x 109/L | Neutrophilia | |
| Lymphocyte | < 1.5 x 109/L | Lymphocytopenia |
| > 3.5 x 109/L | Lymphocytosis | |
| Monocyte | < 0.2 x 109/L | Monocytopenia |
| > 0.8 x 109/L | Monocytosis | |
| Eosinophil | < 40 x 109/L | Eosinopenia |
| > 350 x 109/L | Eosinophilia | |
| Basophil | < 0.01 x 109/L | Basopenia |
| > 0.1 x 109/L | Basophilia |

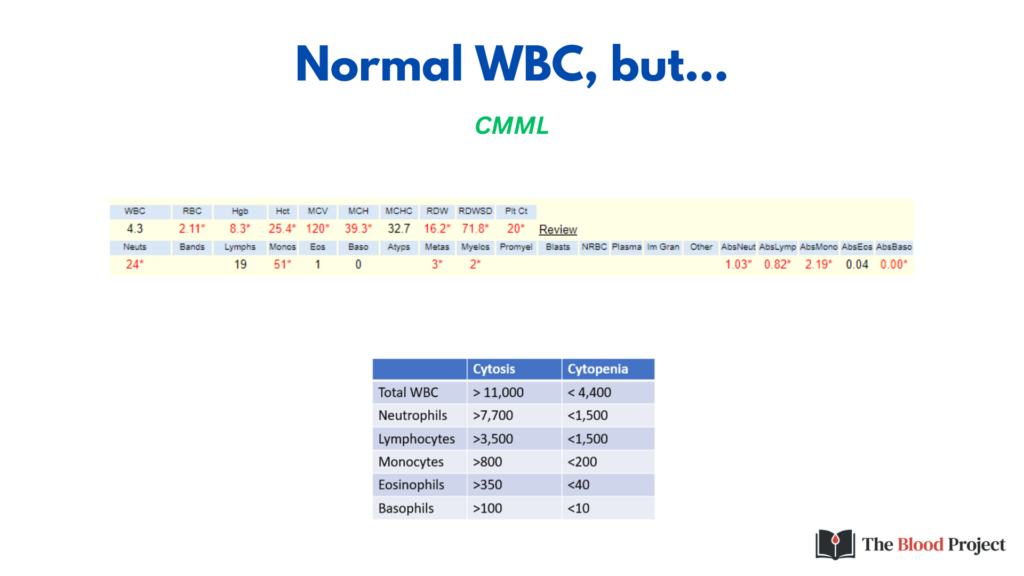

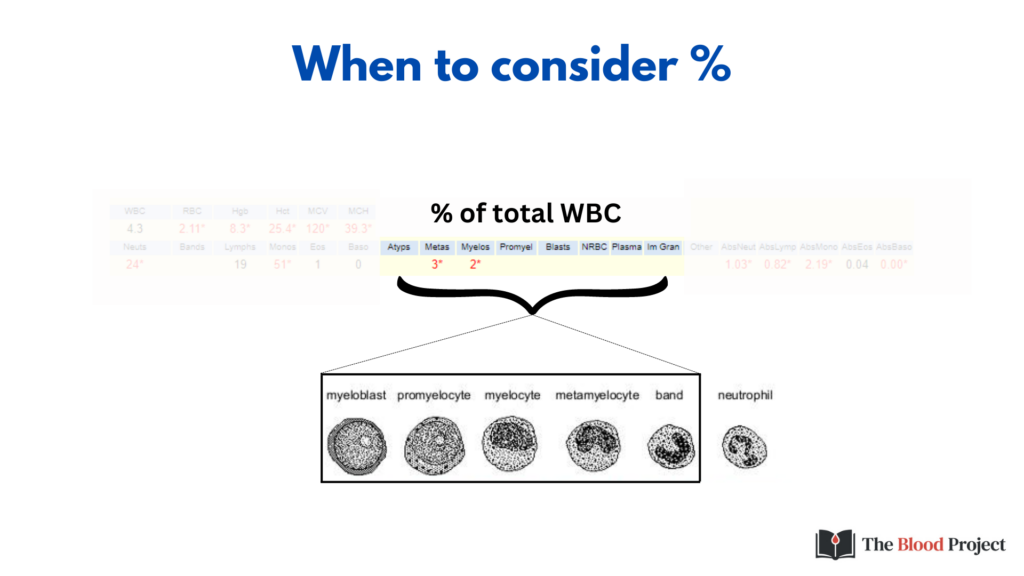
While it is preferable to use absolute counts in the case of neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils and basophils, it is more common to refer to percentages when dealing with less mature forms of WBC in the blood because:
- The absolute numbers are usually very small.
- The mere presence of these immature forms, regardless of their absolute number, often has clinical significance.
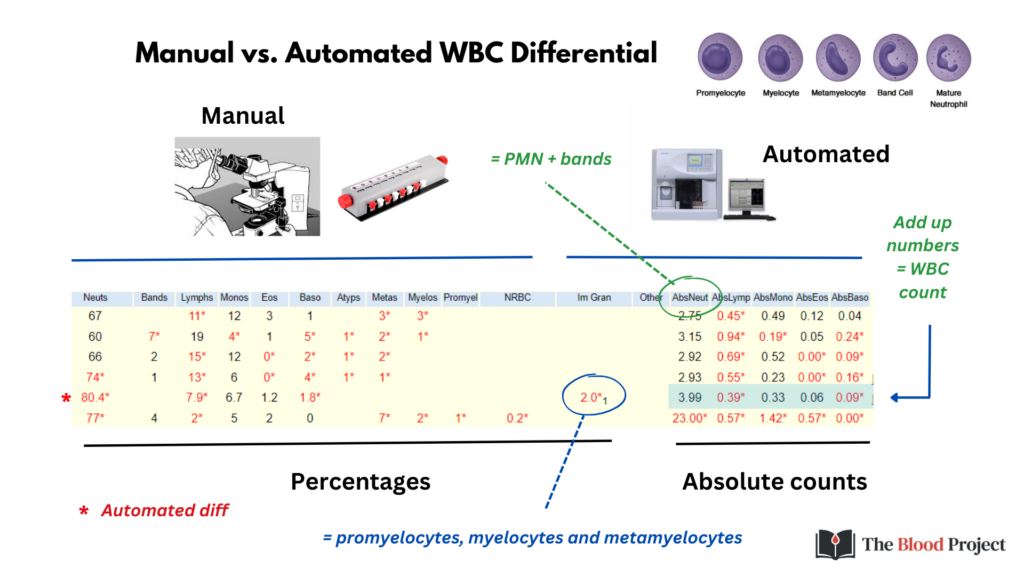
There are two ways of preforming a WBC differential:
- Manual – includes counts for:
- 5 mature cell subtypes
- Each of the immature granulocytes, including
- Promyelocytes
- Myelocytes
- Metamyelocytes
- Bands
- Hematology analyzer – includes counts for:
- 5 mature cell subtypes and
- Immature granulocytes, which include
- Promyelocytes
- Myelocytes
- Metamyelocytes
- [Bands get counted as neutrophils]