E/Z and Cis/Trans Alkenes
In the previous post, we talked about the cis and trans designation of alkenes. As a recap, cis and trans stereoisomerism depends on whether two identical alkyl groups on the c=c bond are on the same or opposite sides of that double bond:

The cis and trans approach works only if two identical groups are connected to the double bond.
To illustrate this limitation, let’s consider two isomeric alkenes having four different groups on the double bond:

We cannot classify these as cis or trans because none of the two groups on the double bond are identical. However, there should be a way of distinguishing them since they are not identical.
And this is where the E and Z designation is used.
Determining E and Z Configuration
So, how is the E and Z configuration of a double bond determined?
It is determined based on the priorities of the groups on the double bond:

Here is the principle; you need to look at each carbon of the double bond separately. And the goal is to first determine which of the two groups on each carbon has a higher priority.
The priorities are assigned following the same rules for the R and S configuration.
For example, we have seen that this alkene cannot be classified as cis or trans but is it E or Z?

Let’s first focus on the left carbon. It has an ethyl group and Cl connected to it. The Cl has a higher priority because of its atomic number:

On the right carbon, we need to compare a hydrogen with a Br atom. Clearly, the Br has a higher priority:

Finally, determine whether the higher priority group on each carbon is on the same or opposite side of the double bond. Since Cl and Br are pointing up and down, they are on opposite sides and the alkene has an E configuration:

You may wonder how the Z configuration of this alkene would’ve looked like. Right below:

How do I remember that it is Z when the groups are on the same and E when they are on opposite sides?
Use this handy trick: Z stands for Zame-they are on the zame side. This might be enough to figure out the E as well, however, you go with E as Epposite sides of the double bond.
What is the relationship of E and Z alkenes?
Just like the cis and trans, E and Z alkenes are stereoisomers and because they are not mirror images, they are diastereomers:

This explanation is covered in more detail using the cis and trans designation.
Additionally, there is a separate article about determining whether a pair of molecules represents identical compounds, constitutional isomers, enantiomers or diastereomers. That is if you need to refresh stereochemistry a little bit.
E and Z when the Same Atom is Connected to the Double Bond
There might be a situation where two or more atoms connected to the double bond are the identical and it is not possible to assign the priorities right away.
For example, let’s consider the following alkene:

On carbon 1, the chlorine is the first priority since it has a higher atomic number than carbon:

However, there are to carbon atoms connected to carbon 2 and the priority cannot be determined solely based on their atomic number:

What do we do?
Just like in the R and S configuration, when there is a tie, you need to look at the atoms connected to the ones being compared.
The carbon on the top (isopropyl group) is connected to two carbons and one hydrogen.

The carbon on the bottom (ethyl group) is connected to a carbon and two hydrogens. Therefore, isospory gets the higher priority.
So, we have the two higher priority groups (Cl and isopropyl) on opposite sides of the double bond as one is pointing down and the other one is pointing up.
This arrangement makes an E alkene:

Naming E and Z Alkenes
The E and Z designation for the configuration of a double bond is also included in the nomenclature of alkenes.
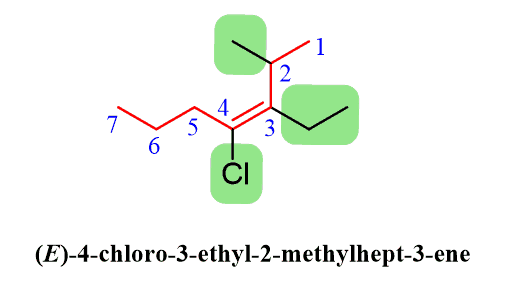
As an example, let’s name the alkene for which we have just determined the E/Z configuration above:

First, determine the name according to the IUPAC rules. The parent chain is heptane and there are three substituents:

Additionally, the configuration of the alkene is placed before the systematic name:
Below are some practice problems for determining the E and Z configuration of alkenes:
Practice
Determine if each of the following alkenes has an E or Z configuration:

This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems including over 20 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems including over 20 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems including over 20 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems including over 20 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems including over 20 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems including over 20 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems including over 20 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems including over 20 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems including over 20 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is for registered users only.
By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the answers and solutions for all the Practice Problems including over 20 hours of problem-solving videos, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Puzzles, and the powerful set of Organic Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Check Also
Alkenes: Structure, Stability and Nomenclature
Elimination Reactions
- SN1 SN2 E1 E2 – How to Choose the Mechanism
- Is it SN1 SN2 E1 or E2 Mechanism With the Largest Collection of Practice Problems
- General Features of Elimination
- The E2 Mechanism
- Zaitsev’s Rule – Regioselectivity of E2 Elimination Reactions
- Stereoselectivity of E2 Elimination Reactions
- Stereospecificity of E2 Elimination Reactions
- Elimination Reactions of Cyclohexanes with Practice Problems
- The E1 Mechanism: Kinetcis, Thermodynamics, Curved Arrows and Stereochemistry with Practice Problems
- Stereoselectivity of E1 Reactions
- Nucleophilic Substitution vs Elimination Reactions
- Regioselectivity of E1 Reactions
- E2 vs. E1 Elimination Mechanism with Practice Problems

good short note