Happy New Year! Let’s make this the year of the dragon!
Snawfus

The Snawfus is an albino deer from the folklore of the Ozarks in Arkansas and Missouri. It has supernatural powers but is not dangerous. Some say it can jump into the treetops with ease, while others grant it feathery wings that along with to fly without making a sound, much like an owl. Some accounts give it flowering boughs for antlers.
Leila A. Wade of Republic, Missouri, extensively studied the snawfus, and reported that it gave off spirals of blue smoke. The blue smoke emitted by the snawfus drifted off and cloaked the Ozark hills in a magical blue haze, which can still be seen in autumn.
References
Randolph, V. (1950) Fabulous Monsters in the Ozarks. The Arkansas Historical Quarterly, 9(2), pp. 65-75.
Rayburn, O. E. (1960) Some Fabulous Monsters and Other Folk Beliefs from the Ozarks. Midwest Folklore, 10(1), pp. 27-32.
Tripodero
Variations: Collapsofemoris geocatapeltes (Cox)

The Tripodero of the Californian chaparral and foothills defies all scientific attempts at classification. Its small, strong body stands on two telescopic legs, with a kangaroo-like tail balancing it behind. As its legs can be collapsed or extended at will, the tripodero can stand tall over the brush, or crawl easily through the undergrowth. The tripodero’s face is all nose, with a storage pouch in its left jaw.
When a tripodero sees potential prey from its elevated vantage point, it sights down its snout and fires a clay slug, a supply of which is kept in a cheek pouch. Tripoderos have perfect aim and shoot with pinpoint accuracy. The clay pellet stuns the victim, allowing the tripodero to come in and devour it, bones and all.
Unlike other fearsome critters, the tripodero is associated primarily with construction sites, railroads, and engineering projects.
References
Brown, C. E. (1935) Paul Bunyan Natural History. Madison, Wisconsin.
Cox, W. T. (1910) Fearsome Creatures of the Lumberwoods with a Few Desert and Mountain Beasts. Judd and Detweiler, Washington D. C.
Dorson, R. M. (1982) Man and Beast in American Comic Legend. Indiana University Press, Bloomington.
Tryon, H. H. (1939) Fearsome Critters. The Idlewild Press, Cornwall, NY.
Crowing Crested Cobra
Variations: Njoka Tambala (Malawi); Bubu (Shupanga, Mozambique); Hongo (Ngindo); Indlondlo (Zulu); Inkhomi (“Killer”, Nyakyusa); Kovoko (Nyamwezi); Limba (Chitipa District, Malawi); Nguluka (Chitipa District, Malawi); Ngoshe (Bemba); Noga-putsane (“Goat-snake”, Botswana); Songo, Songwe (Yao); Black Mamba, Dendroaspis polylepis
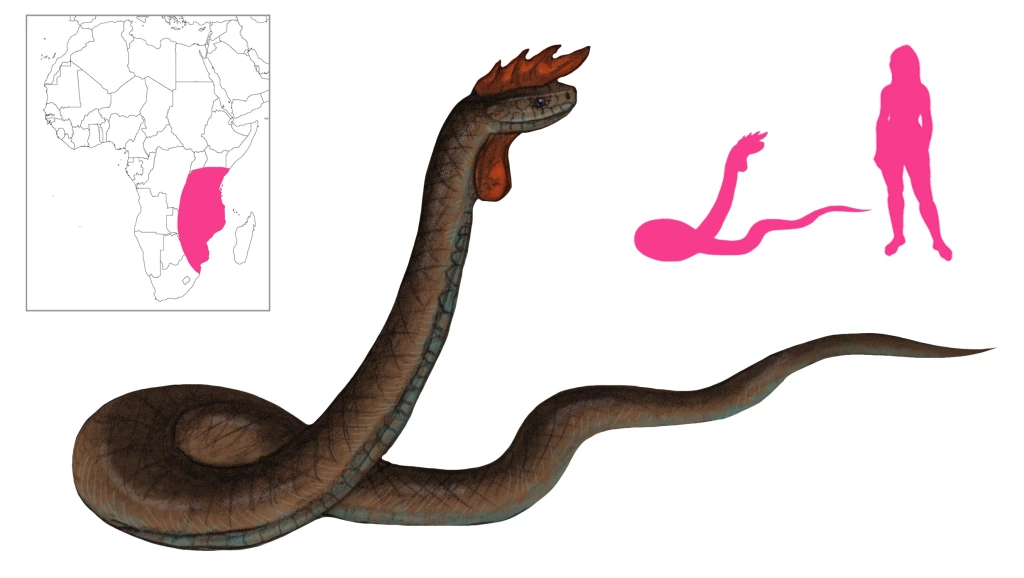
Crowing Crested Cobra is a blanket term used for a number of crested, noise-making venomous snakes. It is one of the most widespread legends in East African folklore, and it is also known from the West Indies, especially Jamaica and Santo Domingo.
A crowing crested cobra is a snake similar to a cobra with a crest on its head and capable of making sounds like a rooster. Those sounds range from crowing to clear bell-like notes to bleating. Sometimes wattles are present as well. The snake is venomous and very dangerous.
Livingstone reported the death of a little girl in Mozambique caused by an enormous snake that dashed at the child, bit her, and made off into a hole. This snake was known as Bubu to the people of the area, and they describe it as twelve feet long, dark with a dirty blue color under its belly, and with red markings on its head like the wattles of a rooster. It will hide in a tree and strike passers-by one after the other, killing them in short order. To protect against it, a pot of boiling water or porridge should be carried on the head. The snake will try to bite that and kill itself in the process, or at least get scalded and discouraged from future attempts. Nonetheless, Livingstone admits that one “will probably recognize the Mamba in this snake”. He also makes separate mention of another, different snake that makes a sound like the crowing of a cockerel, adding that “this is well authenticated”.
Shircore claimed to have in his possession the bony skeleton of the fleshy comb as well as part of the neck with some vertebrae in it, five lumbar vertebrae, and a single 22-mm by 16-mm dorsal vertebra from a very large snake. He describes the crowing crested cobra as growing 18 to 20 feet long. It is buff-colored, with a red crest that points forward. The male has wattles as well. There is no hood like a cobra’s. The head is small for the size of the body, while the bones of the skull are denser than usual. It moves very fast and can climb trees. The male crows like a rooster, while the female clucks, te te te te. Both sexes make a warning sound, chu chu chu chu, repeated rapidly. Shircore also attributes to the crowing crested cobra or Inkhomi a diet of maggots, explaining that it kills indiscriminately to create more food for maggots. It is tolerated around villages, where mutual respect keeps it and humans apart. It is also intimately associated with sorcery and witchcraft; chieftains and witch doctors wear pieces of it, and parts of its body are used in curative preparations. Parts of the snake in mixtures amplify the potion’s effects. Shircore gives it a range of the lower Zambezi in the South to Victoria Nyanza in the North, Lake Tanganyika in the West, and the Indian Ocean in the East.
Loveridge equates the crowing crested cobra with the black mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis). Tellingly, he also gives songo and songwe as the native names of the black mamba – and Shircore also gives songo as the name of the crowing crested cobra.
Similarly vocal snakes are found throughout East Africa. The Limba of Malawi is crested and crows. It can be found in the Mafinga Ridge. The fierce Nguluka has the head of a snake on the body of a guineafowl. Noga-putsane, the “goat snake” or “serpent of a kid”, bleats like a goat to attract its victims. Livingstone claimed to have heard one calling from a spot where no kid could have been. The Zulu plumed viper Indlondlo is also known to bleat. Finally, even the umdlebe or dead man’s tree, said to kill anyone that approaches it and strike birds dead in flight, is said to bleat like a goat!
Rationalizations for the combinations of features include a snake trying to eat a loudly protesting rooster, and a snake that was sloughing its skin, with pieces of dead skin giving the impression of a crest and wattles around the head. The snake and rooster are strongly involved in voodoo belief, which give a cultural background to the creature. The resemblance to the basilisk is also notable.
Calls attributed to the crowing crested cobra are usually the work of rails. These are small, retiring birds with a tendency to call at dusk or at night. Flufftails in particular have particularly haunting calls. The call of the buff-spotted flufftail (Sarothrura elegans) has been connected to the crowing crested cobra, as well as to banshees, to a chameleon giving birth, to a chameleon mourning for its mother which it accidentally killed in a squabble over mushrooms, and to giant snails.
References
Collins, W. B. (1959) The Perpetual Forest. J. B. Lippincott Company, Philadephia.
Hargreaves, B. J. (1984) Mythical and Real Snakes of Chitipa District. The Society of Malawi Journal, Vol. 37, No. 1, pp. 40-52.
Hichens, W. (1937) African Mystery Beasts. Discovery (Dec): 369-373.
del Hoyo, J.; Elliott, A.; and Sargatal, J. (eds.) (1996) Handbook of the Birds of the World vol. 3. Lynx Edicions, Barcelona.
Livingstone, D. (1857) Missionary Travels and Researches in South Africa. John Murray, London.
Loveridge, A. (1953) Zoological Results of a Fifth Expedition to East Africa III: Reptiles from Nyasaland and Tete. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College, 110(3), pp. 143-322.
Parker, H. W. (1963) Snakes of the World. Dover Publications, New York.
Shircore, J. O. (1944) Two Notes on the Crowing Crested Cobra. African Affairs, 43(173), pp. 183-186.
Stuart, C. and Stuart, T. (1999) Birds of Africa. The MIT Press, Cambridge.
Waller, H. W. (1874) The Last Journals of David Livingstone in Central Africa, v. II. John Murray, London.
Witkəś
Mammoth thanks to Schnellegeister Hexenwolf for sharing Mansi Mythology with me and making this entry possible!
Variations: Witkəś-ōkja (male), Witkəś-ēkwa (female); Witkul’, Witkul’-ōkja (male), Witkul’-ēkwa (female)

The Witkəś is a creature from the mythology of the Mansi people of Russia. It is one of the few mythical creatures unquestionably derived from paleontological evidence – in this case, from the remains of woolly mammoths. Witkul’ is a synonym, apparently related to locality – witkul’ are found in lakes, and witkəś in rivers.
The name of the witkəś or witkul’ is derived from wit, “water”. A witkəś lives in the depths of the water, as evidenced by the location of mammoth tusks and bones on riverbanks. The tusks were believed to be antlers, shed by the witkəś much like reindeer and elk do. Since there are witkəś bones in evidence, the witkəś themselves are believed to be mortal creatures that avoid contact with humans. Their shapes are undefined, with some traditions anthropomorphizing them, dividing them into male witkəś-ōkja and female witkəś-ēkwa. They have been known to invite guests underwater to drink tea.
Along the Sos’va River it was believed that old bears and elks would gorge themselves on earth, then sink into the water to become water spirits. In lakes they would become witkul’, while in rivers they became witkəś.
The witkəś and witkul’ are tireless diggers, excavating holes and river channels to direct the course of the water. A witkul’-ēkwa was believed to have dug out the Lyapin River, and a witkul’-ōkja made the big lakes of the Sos’va River. On the other hand, the witkəś on the Tavda River would pull horses into the water, and its appearance was an omen of impending death.
Nobody fishes in lakes where witkul’ live. Even birds fly around them. Any living creature that comes near may be pulled in. A witkəś can be found in every whirlpool in a river, and they enjoy drowning anyone who enters their domain. One way to scare off or kill a witkəś is to fill a boat with salt, pitch, and gunpowder, and set up a scarecrow decoy for good measure before setting the boat on fire and pushing it out to the whirlpool to be swallowed. The witkəś will be fatally maimed by the explosive boat, and when its dying groans are heard, that is when it is safe to return to the water.
Around Berezovo it was traditional to sacrifice a reindeer to the witkəś at the time the ice began to drift, tossing the skin, bones, and blood of the animal into the whirlpool. Elsewhere items such as copper cauldrons would be tossed into whirlpools as offerings to the witkəś. Once an old man stole a silk handkerchief with silver coins that was meant for the witkəś. His boat was immobilized, and a witkəś over ten meters long appeared, accusing the man of theft. The kerchief was thrown into the water, and the boat began moving again immediately.
References
Napolskikh, V., Hoppál, M., and Siikala, A. (2008) Mansi Mythology. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest.
Questing Beast
Variations: Beste Glapissante; Beste Glatissant, Bête Glatissante, Glatisant Beast; Beste Diverse, Bête Diverse, Diverse Beste, Diverse Beast; Besta Ladrador, Besta Desasemelhada (Portuguese, from the Demanda); Barking Beast, Yelping Beast
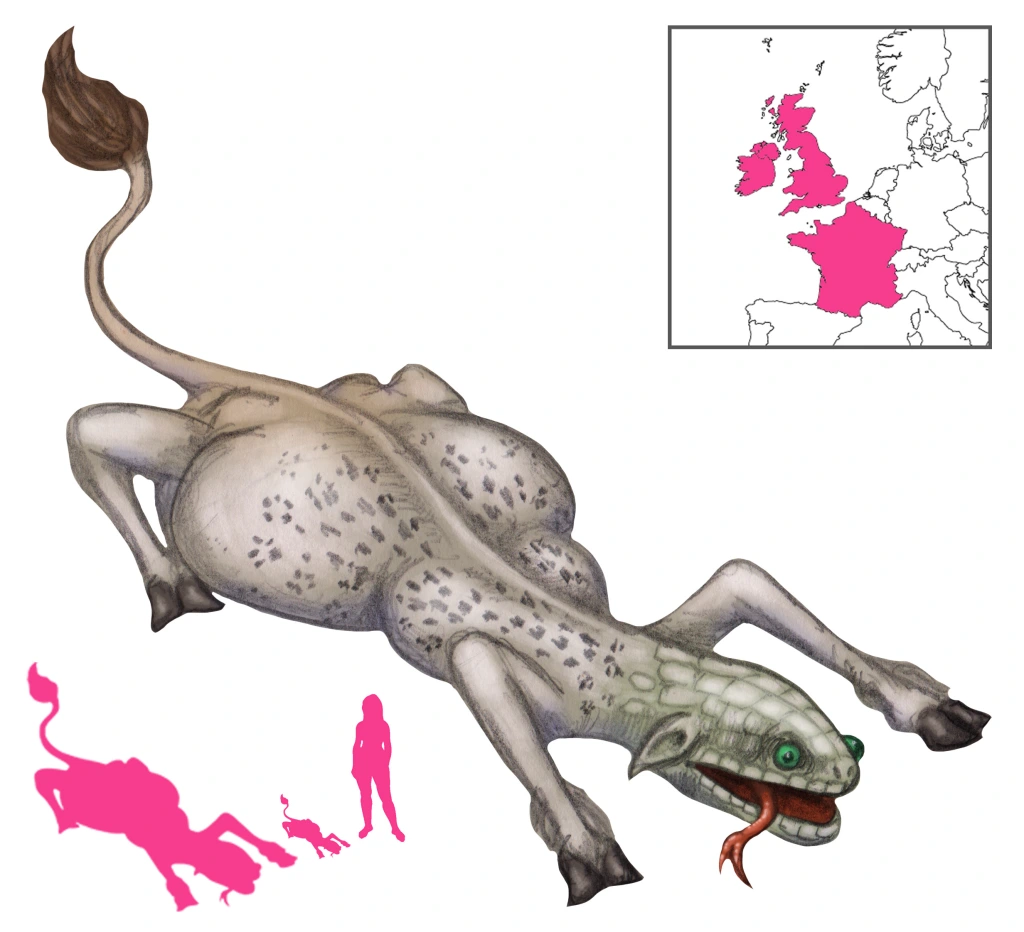
The Questing Beast is a creature of many names, sizes, and appearances. Several features, however, are consistent throughout its appearances in Arthurian legend. First, it very noisy, its offspring within its belly baying and yelping constantly. It is also always a portentous creature, but what it symbolizes has varied from author to author. Finally, it is commonly pursued or hunted, whether by knights or by its own offspring within its belly, and often ends up giving birth in the process.
Although “Questing Beast” has been popularized in the English-speaking world by Malory’s Le Morte d’Arthur, the creature is more commonly known as the Beste Glatissant or Beste Glapissant (in modern French, Bête Glatissante or Bête Glapissante). Glatir or glapir refers to the sound coming from the creature’s belly, a yelping or baying sound like those of hounds chasing prey. This is also the definition of “questing”; a more accurate modern name would be the Yelping Beast or Barking Beast.
The concept of noisy animals in their mother’s womb precedes the Questing Beast. William of Malmesbury describes a dream that was had by King Eadgar. In it, the king sees a pregnant hunting dog lying at his feet. She was silent, but the pups in her womb were barking loudly. This was interpreted as meaning that after King Eadgar’s death, miscreants within his kingdom would bark against the church of God. In the Slavic Twelve Dreams of Sehachi, the titular character dreams of a foal neighing within a mare’s belly, and whelps barking in a dog’s belly; these are interpreted as mothers acting immodestly with their daughters and children rejecting the advice of their parents, respectively.
Another contributor to the genesis of the Questing Beast is the supernatural boar hunt. The most famous examples of those are the boar Twrch Trwyth and the sow Henwen. The latter is even more closely connected to the Questing Beast; like the Beast, Henwen (“Ancient White”) is white in color, and dangerously fecund. Her offspring were to be harmful to Britain, so she was hunted across the country, giving birth along the way to various young. Finally, Henwen disappeared into the sea at Penryn Awstin, similar to the stricken Questing Beast diving into a lake.
The oldest iterations of the Questing Beast have it encountered by Perceval over the course of his search for the Grail. In the Perlesvaus, Perceval finds a beautiful glade, with a red cross at the center of it. A knight dressed in white is seated at the far end of the glade, with a fair young damsel next to him. Soon a snow-white, emerald-eyed creature, between a fox and a hare in size, enters the glade. The whelps in its womb are barking like hounds, and it is terrified and agitated because of that. Perceval tries to take the small Beast onto his horse, but he is cautioned by the knight, who tells him the Beast has a destiny to fulfill. The Beast runs to the cross, where its twelve young are brought forth. They immediately tear their mother to pieces, but can only devour her head. Upon doing so, they go mad and scatter into the forest. King Pelles later explains the significance of the creature to Perceval: it represents Jesus Christ, and the twelve hounds that killed it and scattered are the twelve tribes of Israel, following the prevalent Christian belief of the time.
Gerbert de Montreuil’s continuation of Perceval borrows from the Perlesvaus. We are not given a description of the Beast, but are instead told that it is grant a merveille (“marvelously large”). The Beast’s young are barking and yelping from within its belly, and when it comes up to the cross in the glade, they emerge violently, breaking it in two pieces. The young then devour their mother before going mad, turning on and killing each other. This bloody episode has a far more mundane meaning – Perceval is told that the loud, murderous whelps are the people who disturb church services by talking loudly and complaining about hunger!
In the Estoire du Saint Graal, there is a Beste Diverse (“Diverse Beast”) found beside a cross. No mention is made of its yelping, but it is white as snow, and has the head and neck of an ewe, the legs of a dog, black thighs, the body of a fox, and the tail of a lion. In the prose Merlin, the Diverse Beste or Beste Diverse sounds like 30 or 40 baying hounds and is moult grant (“very big”). Perceval is destined to hunt it.
In the prose Tristan, the Beste Glatissant has the legs of a stag, the thighs and tail of a lion, the body of a leopard, and the head of a snake; its yelping is equal to that of a hundred hunting hounds. The addition of snake, leopard, and lion elements grant it unsavory connotations; the combination of lion and leopard is reminiscent of the Beast of the Apocalypse, and a snake or dragon is always inauspicious.
No longer a creature of purity torn apart by its own offspring, the Questing Beast is now an evil, wretched being spawned from violence. Its mother was the daughter of King Ypomenes, who lusted for her brother. When she could not have him, she instead turned to a devil, who slept with her and convinced her to accuse her brother of attempting to rape her. He was duly sentenced to be torn apart by dogs. As he died, the brother proclaimed that his sister would give birth to a monster, one from whose belly the barking of dogs would forever remind others of his shameful death. As predicted, the daughter gave birth to the Questing Beast, and she was executed for her crimes.
The Saracen knight Palamides had particular reason to hate the Questing Beast, as its horrid shriek had killed eleven of his twelve brothers. In the Portuguese Demanda, the Questing Beast is finally slain during the last years of the Grail quest, when Palamides strikes it and it runs into a lake that immediately starts to boil. The lake has since then become known as the Lake of the Beast.
Malory’s Le Morte d’Arthur, the foremost mention of the Questing Beast in English literature, follows the prose Tristan in its description. The Questing Beast is said to have a head like a serpent’s, a body like a leopard’s, buttocks like a lion’s, and feet like a hart. Its belly made a noise like thirty couple hounds barking. King Arthur first sees the Questing Beast after an illicit tryst with the wife of King Lot of Orkney. Arthur had stopped to rest by a well when the Questing Beast, making a horrid din, came up to drink from it. As it drank, the noise coming from its belly was quelled, but it started up against as soon as the creature had finished and ran off. Arthur then encountered Sir Pellinore, who hunted the Questing Beast. After Pellinore’s death, the task of hunting the Questing Beast was passed on to Sir Palamides.
Merlin later revealed to Arthur the significance of the Questing Beast. The king had seen the beast because he, too, had just done something unforgivable. The wife of King Lot was in fact his sister on his mother’s side, and the child of this adulterous and incestuous union – Mordred – was destined to destroy Arthur’s kingdom.
References
Evans, S. (1903) The High History of the Holy Graal. J. M. Dent & Co., London.
Gaster, M. (1900) The Twelve Dreams of Sehachi. Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, pp. 623-635.
Löseth, E. (1891) Le Roman en Prose de Tristan, analyse critique. Emile Bouillon, Paris.
Malory, T. (1956) Le Morte d’Arthur, v. I. J. M. Dent & Sons Ltd., London.
Malory, T. (1956) Le Morte d’Arthur, v. II. J. M. Dent & Sons Ltd., London.
Nitze, W. A. (1902) The Old French Grail Romance Perlesvaus, A Study of its Principal Sources. John Murphy Company, Baltimore.
Nitze, W. A. (1936) The Beste Glatissant in Arthurian Romance. Zeitschrift für Romanische Philologie, 56, pp. 409-418.
Paris, G. and Ulrich, J. (1886) Merlin: Roman en Prose du XIIIe Siècle, t. I. Librairie de Firmin Didot et Cie., Paris.
Pickford, C. E. (1959) L’evolution du Roman Arthurien en Prose vers la Fin du Moyen Age. A. G. Nizet, Paris.
Williams, M. (1925) Gerbert de Montreuil: La Continuation de Perceval, t. II. Librairie Ancienne Honoré Champion, Paris.
Wakmangganchi Aragondi
Variations: Wakmabitchi Warak Wakkimbi (“Primordial Head of the Strong-Teethed Swine Family”)

Wakmangganchi Aragondi was the greatest and most terrifying monster in the folklore of the Garo people of India. This primordial demon once lay waste to the Garo Hills before it was slain by the god Goera.
Long before Goera’s birth, his maternal uncles descended into the subterranean region along with the fisherman Gonga Tritpa Rakshanpa and his dog. From there they took the progenitor of all the world’s birds back to the surface. The three uncles also brought with them a little pig, which they named Wakmabitchi Warak Wakkimbi.
The tiny piglet was kept in sty made of rocks, and there it grew and grew, until the sty had to be torn down to set it free. By then the pig was so big it could no longer be controlled; it wandered at will, feeding wherever and whenever it liked. People continued to feed it from a safe distance, until the day when it knocked the three uncles into its feeding trough and ate them alive. From then on, nobody dared approach it, and it continued to grow and increased in power. From then on it became known as Wakmangganchi Aragondi.
The mere mention of Wakmangganchi Aragondi was enough to strike fear into the bravest warrior – and with good reason. The colossal boar was the biggest and mightiest creature in the world, as tall as a mountain. When standing up, Wakmangganchi Aragondi’s snout touched the Dura Hill, while its tail lay in the Songdu River. It had seven heads emerging from its neck, each head with seven tusks like double-edged scimitars, and each head with a single piercing eye in its forehead glowing like the full moon. On Wakmangganchi Aragondi’s back grew seven clumps of bamboo, seven plots of thatch grass, and seven stalks of bulrushes. Seven perennial streams flowed down its back. The microcosm on Wakmangganchi Aragondi’s back was home to a pair of langurs and their offspring, and seven pairs of moles.
Wakmangganchi Aragondi roamed where it pleased, ate anyone it encountered, and destroyed crops at will. It had a particular fondness for gourds, melons, pumpkins, and yams. Nobody could stop it.
Such was the monster that Goera faced. When the hero-god was born, two more of his uncles went to the market to buy a goat, but they were intercepted and devoured by Wakmangganchi Aragondi. Thus Goera, upon coming of age, decided to destroy this plague that terrified his people.
To fight Wakmangganchi Aragondi, Goera sought the aid of the giant crab Songduni Angkorong Sagalni Damohong. He used it to threaten his grandmother into telling him all she knew about Wakmangganchi Aragondi. He then befriended various supernatural beings, including the progenitors of Steel and Dolomite. From Dygkyl Khongshyl, the smith-god, he obtained a magical two-edged milam sword and a magical bow and arrows that could shatter trees and cure disease. He allied with Tengte Kacha, king of the Elfs, and Maal the dwarf god – both barely two cubits tall, but possessed of great magical powers.
Now fully armed, Goera set out to find Wakmangganchi Aragondi. He found the gigantic boar wallowing in mud, asleep, at Ahnima Gruram Chinima Rangsitram. Goera sent his servant Toajeng Abiljeng to strike the boar from behind and awaken it.
Wakmangganchi Aragondi awoke in fury, and charged Goera. But the hero-god stood his ground and fired a hail of burning darts at it. That was too much for the monster, and Wakmangganchi Aragondi ran for the first time. It galloped east, with Goera in pursuit firing volleys of arrows that lacerated its body. Then Wakmangganchi Aragondi turned north, then back, making wild sallies across the region, making the whole world rumble and quake.
Maddened beyond reason by pain and rage, Wakmangganchi Aragondi tried at last to turn on its tormentor, but Goera avoided its charges by creating piles of rock to climb and hide on. Finally, one of Goera’s maternal uncles in the subterranean region shot an arrow through Wakmangganchi Aragondi’s armpit. The monster staggered and finally collapsed at Ahguara Rongpakmare Shohlyng Janthihol. There Goera decapitated it with a triumphant cry.
The battle had taken seven summers and seven winters. When Wakmangganchi Aragondi was cut open, Goera’s two uncles were found inside, alive but blinded. They recovered their eyesight with time. The meat of Wakmangganchi Aragondi was divided among the people of the area, with the rest left to decompose.
The rock piles created during the battle can still be seen. They are known as Goerani Ronggat, the “Stone Piles of Goera”. Wakmangganchi Aragondi’s droppings are rocks in which seeds can still be seen, and red areas of land are where the monster-boar’s blood was spilled.
References
Bhairav, J. F. and Khanna, R. (2020) Ghosts, Monsters, and Demons of India. Blaft Publications, Chennai.
Rongmuthu, D. S. (1960) The Folk-tales of the Garos. University of Gauhati Department of Publication, Guwahati.